dinov2 第一主成分特征可视化
DINOv2是由 Meta AI 提出的第二代自监督视觉变换器模型(Vision Transformer)。该模型在没有人工标签的情况下,通过自监督学习技术,能够从海量无标注图像中学习有意义的表示。DINOv2在图像分类、目标检测、语义分割等任务上都表现出了优异的性能。dinov2演示中有一个将图像特征的三个第一主成分的可视化,映射到RGB值,本文通过google 用以实现该可视化功能。
·
DINOv2 是由 Meta AI 提出的第二代自监督视觉变换器模型(Vision Transformer)。该模型在没有人工标签的情况下,通过自监督学习技术,能够从海量无标注图像中学习有意义的表示。DINOv2 在图像分类、目标检测、语义分割等任务上都表现出了优异的性能。
dinov2演示中有一个将图像特征的三个第一主成分的可视化,映射到RGB值,本文通过google 用以实现该可视化功能
0.加载 dinov2 模型
首先确保git clone 了官方代码库,亦或是从torch中加载
import os
import torch
import torchvision.transforms as T
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
#import hubconf ## Load the largest dino model (git clone)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
# DINOv2 load from torch.hub
dino = torch.hub.load('facebookresearch/dinov2', 'dinov2_vitb14')
# Load the largest dino model (git clone)
#dino = hubconf.dinov2_vitg14( )
dino = dino.cuda()
总而言之,运行后会下载权重
1.加载图像
将图像放在img_dir指向的文件夹下
# 图像目录路径
img_dir = 'test_img/'
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
# 加载图像并确保它们是 RGB 格式
image_files = os.listdir(img_dir)
images = []
for image in image_files:
img = Image.open(os.path.join(img_dir, image)).convert('RGB')
images.append(img)
img_shape = 560
# 定义预处理管道
transform = T.Compose([
T.Resize(img_shape, interpolation=T.InterpolationMode.BICUBIC),
T.CenterCrop(img_shape),
T.ToTensor(),
T.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
# 批量大小
batch_size = min(len(images), 5) # 确保批次大小不超过图像数量
imgs_tensor = torch.zeros(batch_size, 3, img_shape, img_shape)
# 预处理图像并转换为张量
for i, img in enumerate(images[:batch_size]):
imgs_tensor[i] = transform(img)[:3]
# 将图像张量传递到CUDA
imgs_tensor = imgs_tensor.to(device)
# 推理
with torch.no_grad():
features_dict = dino.forward_features(imgs_tensor)
features = features_dict['x_norm_patchtokens']定义一个显示图像的函数:
def imshow(tensor, title=None):
# 反归一化
mean = torch.tensor([0.485, 0.456, 0.406])
std = torch.tensor([0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
tensor = tensor * std[:, None, None] + mean[:, None, None]
# 转换为 numpy 数组并转置维度
np_image = tensor.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0))
# 限制到 [0, 1] 范围
np_image = np.clip(np_image, 0, 1)
# 显示图像
plt.imshow(np_image)
if title:
plt.title(title)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()我们展示第一张图如下
imshow(imgs_tensor[0].cpu(), title='Image 1')
2.PCA
使用pca进行处理
# Compute PCA between the patches of the image
features = features.reshape(batch_size*1600, 768)
features = features.cpu()
pca = PCA(n_components=3)
pca.fit(features)
pca_features = pca.transform(features)
# Visualize the first PCA component
for i in range(batch_size):
plt.subplot(1, batch_size, i+1)
plt.imshow(pca_features[i * 1600: (i+1) * 1600, 0].reshape(40, 40))
plt.show()处理后的图像如下

3.映射RGB
# Remove background
forground = pca_features[:, 0] < 1 #Adjust threshold accordingly
background= ~forground
# Fit PCA
pca.fit(features[forground])
features_forground = pca.transform(features[forground])
# Transform and visualize the first 3 PCA components
for i in range(3):
features_forground[:, i] = (features_forground[:, i] - features_forground[:, i].min()) / (features_forground[:, i].max() - features_forground[:, i].min())
rgb = pca_features.copy()
rgb[background] = 0
rgb[forground] = features_forground
rgb = rgb.reshape(batch_size, 40, 40, 3)
for i in range(batch_size):
plt.subplot(1, batch_size, i+1)
plt.imshow(rgb[i][..., ::-1])
plt.show()最后可视化图像如下,只能说原图特征比较抽象

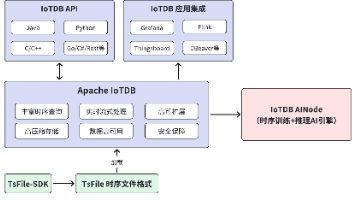
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献1条内容
已为社区贡献1条内容








所有评论(0)