利用Python中的pandas+numpy+openpyxl+matplotlib.pyplot+matplotlib.patches+正则表达式等模块对xlsx文件进行数据清洗并进行数据可视化分析
在日常工作中,我们经常需要对excel文件中的数据进行清洗,剔除掉我们不需要的数据,抓取我们想要的数据,并把想要的数据保存在新的excel中,再对新的清洗后的excel进行一些数据可视化分析等操作。那在本博文接下来所讲的内容里,我使用pandas、openpyxl、re等模块对数据进行清洗;然后利用pandas、openpyxl把清洗后的数据存在新的excel中;
前言
在日常工作中,我们经常需要对excel文件中的数据进行清洗,剔除掉我们不需要的数据,抓取我们想要的数据,并把想要的数据保存在新的excel中,再对新的清洗后的excel进行一些数据可视化分析等操作。那在本博文接下来所讲的内容里,我使用pandas、openpyxl、re等模块对数据进行清洗;然后利用pandas、openpyxl把清洗后的数据存在新的excel中;最后利用matplotlib.pyplot、matplotlib.patches、re、datetime、os、glob等模块对清洗好的数据表格进行数据可视化分析。本文中所讲的代码绘制的是一些工程用图,这里不便展示。本文重点介绍代码的逻辑结构和思想,以及对一些细节的处理。
一、项目背景:
在我们的日常工作中,经常会遇到数据很杂乱的表格,而我们想要的数据就分布在这些杂乱的表格中。此时,我们就需要把我们想要的数据从这些杂乱的表格中提取出来,单独存放在我们想要的位置。那么,本博文就从这个角度来深度解析如何实现这一功能!
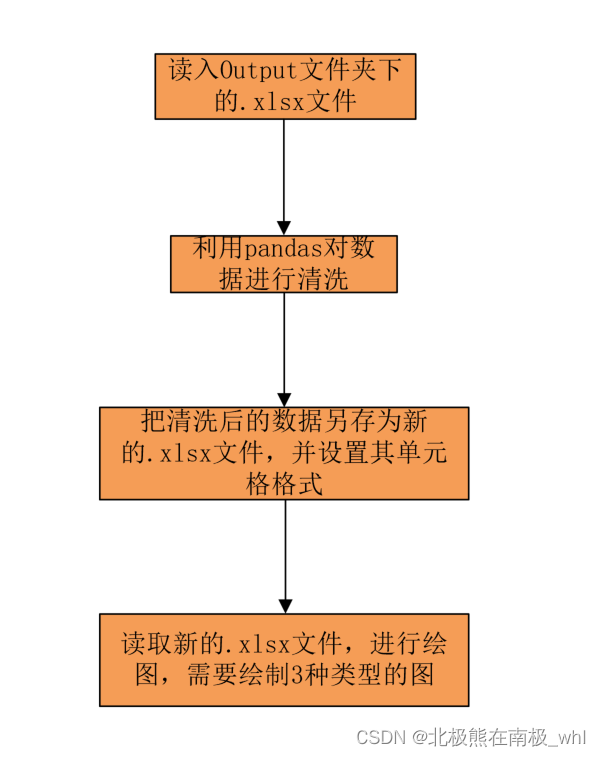
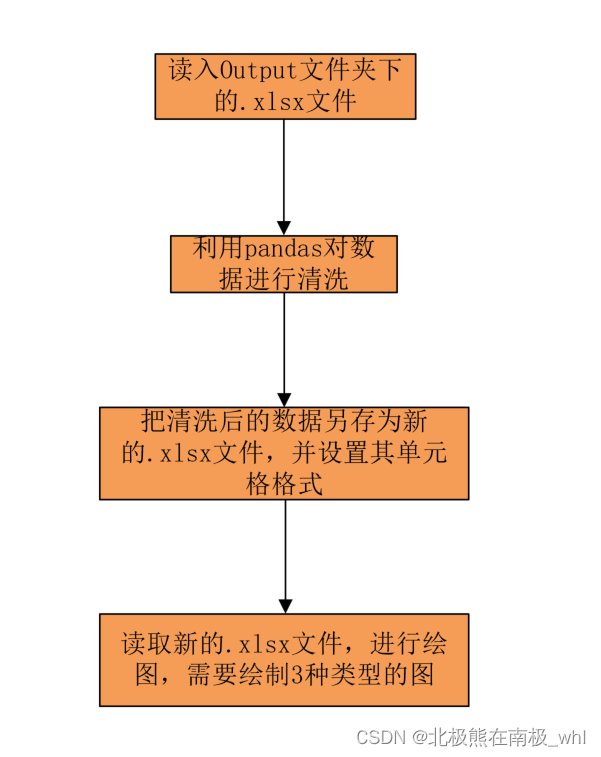
二、输入的.xlsx文件的sheet名样板和脚本主体逻辑架构图:
1.输入的.xlsx文件的sheet名样板

2.脚本主体逻辑架构图
三、脚本功能模块解析
1.引入库
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime as dt
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
import re
import os
import glob
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
2.设置pandas在console的输出模式为显示所有的列
代码如下:
pd.options.display.max_columns = None
3.获取Output文件夹下的.xlsx文件的相对路径
代码如下:
# 获取当前脚本文件所在目录
path_current = os.getcwd()
# 获取当前脚本文件所在目录的上一级目录
path_pardir = os.path.dirname(path_current)
print('$$$path_pardir:', path_pardir)
file_lists = glob.glob(path_pardir + '/Output/*.xlsx')
print('$$$file_lists:', file_lists)
4.初始化定义
代码如下:
# 先定义好需要提取的有效信息的列名
column_common = ['lot_id', 'wf_id', 'die_x', 'die_y', 'SBIN_NUM']
# column_private = ['Istandby:VDD[1]', 'Istandby:VDDI[1]', 'Istandby:VDD_SRAM[1]', 'Istandby:VDDIO[1]',
# 'Scan_HV', 'Scan_MV', 'Scan_LV', 'M6N_HV', 'M6N_MV', 'M6N_LV', 'Data_Retention_0', 'Data_Retention_1']
abnormal_character_set = ['/', '\\', ':', '*', '"', '<', '>', '|', '?']
5.编写一个画圆的函数
代码如下:
def cycle_picture():
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8), dpi=100)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
theta = np.arange(0, 2 * np.pi, 0.01)
x = 5 + 5.5 * np.cos(theta)
y = 4 + 4.5 * np.sin(theta)
# plt.vlines(np.arange(-0.5, 11, 1), -0.5, 8.5, linestyles='--')
# plt.hlines(np.arange(-0.5, 9, 1), -0.5, 10.5)
plt.plot(x, y, color='Black')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
plt.xticks(np.arange(-1, 12, 1))
plt.yticks(np.arange(-1, 9, 1))
ax.invert_yaxis()
# plt.show()
return ax
6.编写一个绘制FBC的函数
代码如下:
def FBC_draw(die_X, die_Y, list_FBC_temp, lot, wafer, list_FBC_item, local_Path):
color_dict = {'1': '#00FF00', '2': '#32CD32', '3': '#90EE90', '4': '#F0E68C', '5': '#FFFF00', '6': '#FFA500',
'7': '#FF8C00', '8': '#FF7F50', '9': '#FF4500', '10': '#FF6347', '11': '#CD5C5C', '12': 'FF0000',
'13': '#8B0000'}
ax = cycle_picture()
for X, Y, FBC_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, list_FBC_temp):
# 以下if结构中用FBC_v的大小来衡量每个die该赋的颜色, 文字, 以及文字大致居中时所需的X轴的坐标偏移量
if FBC_v >= 268435456:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '12'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 67108864 <= FBC_v < 268435456:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '12'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 8388608 <= FBC_v < 67108864:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '9'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 2097152 <= FBC_v < 8388608:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '9'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 1048576 <= FBC_v < 2097152:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '5'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 524288 <= FBC_v < 1048576:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '5'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 104858 <= FBC_v < 524288:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '4'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 1000 <= FBC_v < 104858:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024, 1)
color = '4'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'K'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 100 <= FBC_v < 1000:
pv = FBC_v
color = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 50 <= FBC_v < 100:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 10 <= FBC_v < 50:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 0 < FBC_v < 10:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.1
elif FBC_v == 0:
pv = FBC_v
color = '1'
shift_v = 0.1
else:
pv = FBC_v
color = '12'
shift_v = 0.1
# 画出对应的die的形状Rectangle, 透明度alpha, 表面填充颜色, 边缘线条颜色, 线宽
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[color], edgecolor='k', linewidth=2))
# 画出每个die上的文字, 即需要显示的Fail bit count的大小
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, pv, fontsize=12)
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_FBC_item = str(list_FBC_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
# 画出每片Wafer的标题
plt.text(1, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_FBC_item) + '_FBC_Map', size=14)
# 调整subplot的参数
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
# 保存画好的FBC_Map图, bbox_inches='tight'以紧凑型保存, 并格式化命名
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_FBC_item) + '_FBC_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# ion函数开始matplotlib的交互模式, 即遇到plt.show()函数时会继续执行
# plt.ion()
# plt.show()
plt.close()
7.编写一个绘制ISB的函数
代码如下:
def ISB_draw(die_X, die_Y, list_Isb_temp, lot, wafer, list_Isb_item, local_Path):
color_dict = {'1': '#00FF00', '2': '#32CD32', '3': '#90EE90', '4': '#F0E68C', '5': '#FFFF00', '6': '#FFA500',
'7': '#FF8C00', '8': '#FF7F50', '9': '#FF4500', '10': '#FF6347', '11': '#CD5C5C', '12': 'FF0000',
'13': '#8B0000'}
ax = cycle_picture()
for X, Y, ISB_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, list_Isb_temp):
pv = abs(float(ISB_v))
if 200 <= pv < 999999:
# pv = str(round(pv / 1000, 2)) + 'K' if pv >= 1000 else round(pv, 1)
# pv = round(pv, 1)
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 150 <= pv < 200:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 100 <= pv < 150:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 80 <= pv < 100:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 50 <= pv < 80:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.25
elif 30 <= pv < 50:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 10 <= pv < 30:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '3'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 0 <= pv < 10:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '1'
shift_v = 0.2
else:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '13'
shift_v = 0.2
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[para_v], edgecolor='k',
linewidth=2))
# 画出每个die上的文字, 即需要显示的Fail bit count的大小
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, pv, fontsize=10)
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_Isb_item = str(list_Isb_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
plt.text(1, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_Isb_item) + '_Map', size=14)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_Isb_item) + '_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# plt.ion()
# plt.pause()
# plt.show()
plt.close()
8.编写一个绘制Bin的函数
代码如下:
def Bin_draw(die_X, die_Y, bin, lot, wafer, local_Path):
ax = cycle_picture()
color_dict = {1: '#00FF00', 2: '#FF0000', 4: '#800000', 7: '#FFA500', 8: '#FF4500', 9: '#FFFF00',
10: '#7B68EE', 11: '#800080', 12: '#008080', 13: '#F08080', 14: '#BC8F8F', 15: '#CD5C5C',
16: '#87CEFA', 17: '#D4F2E7', 30: '#DA70D6', 31: '#9932CC', 32: '#0000FF', 36: '#FF00FF',
40: '#00FFFF', 44: '#1E90FF', 48: '#FF69B4', 49: '#FF6347', 66: '#FF69B4'}
for X, Y, bin_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, bin):
# 若First Fail Bin 不在color_dict的键值中, 则一律将其颜色赋值为color_dict中键值42的颜色值
if bin_v in color_dict.keys():
bin_v_index = bin_v
else:
bin_v_index = 66
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[bin_v_index], edgecolor='k', linewidth=2))
shift_v = 0.08 if len(str(bin_v)) == 1 else 0.2
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, bin_v, fontsize=18)
# 画图例
legend = [[1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 30, 31, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 49, 66]]
colcolor = ['#00FF00', '#FF0000', '#800000', '#FFA500', '#FF4500', '#FFFF00', '#7B68EE', '#800080', '#008080',
'#F08080', '#BC8F8F', '#CD5C5C', '#87CEFA', '#D4F2E7', '#DA70D6', '#9932CC', '#0000FF', '#FF00FF',
'#00FFFF', '#1E90EF', '#FF69B4', '#FF6347', '#FF69B4']
plt.table(loc='bottom', cellText=legend, cellLoc='center', colColours=colcolor, rowLabels=['Bin'])
# 画标题
plt.text(3.5, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_Bin_Map', size=14)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_Bin_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# plt.ion()
# plt.show()
# plt.pause()
plt.close()
9.编写主体main函数
代码如下:
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('程序正在运行, 请稍等...')
count = 1
for file in file_lists:
print('=' * 30)
print('正在处理第{}/{}个xlsx文件...'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 清洗.xlsx数据
df_dict = pd.read_excel(file, sheet_name=None)
sheet_name_list = list(df_dict)
# print('$$$sheet_name_list:', sheet_name_list)
sheet_name_sel_list = []
for sheet_name in sheet_name_list:
if re.match(r'.*STDF.*', sheet_name, re.I):
sheet_name_sel = re.match(r'.*STDF.*', sheet_name, re.I)
sheet_name_sel_list.append(sheet_name_sel.group())
# print('$$$sheet_name_sel_list:', sheet_name_sel_list)
######################################################################
# 先提取共通的信息['lot_id', 'wf_id', 'die_x', 'die_y', 'SBIN_NUM']
df_common_sel = df_dict[sheet_name_sel_list[0]]
df_common = df_common_sel[column_common]
# print('$$$df_common:', df_common)
######################################################################
# 再提取非共通的信息['Istandby:VDD[1]', 'Istandby:VDDI[1]', 'Istandby:VDD_SRAM[1]', 'Istandby:VDDIO[1]',
# 'Scan_HV', 'Scan_MV', 'Scan_LV', 'M6N_HV', 'M6N_MV', 'M6N_LV', 'Data_Retention_0', 'Data_Retention_1']
column_private_dict = {}
for sheet_name_var in sheet_name_sel_list:
df_private_sel = df_dict[sheet_name_var]
column_list = list(df_private_sel)
for cols in column_list:
if re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDD\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDDI\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDD_SRAM\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDDIO\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_HV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_MV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_LV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_HV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_MV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_LV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Data_Retention_0.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Data_Retention_1.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
# print('$$$column_private_dict:', column_private_dict)
num = 1
for key in list(column_private_dict):
df_tmp = df_dict[key][column_private_dict[key]]
if num == 1:
df_concat = pd.concat([df_common, df_tmp], axis=1)
else:
df_concat = pd.concat([df_concat, df_tmp], axis=1)
num += 1
# print('$$$df_concat:', df_concat)
# print('$$$list(df_concat):', list(df_concat))
Lot_ID = df_concat['lot_id'][0]
Wafer_ID = df_concat['wf_id'][0]
# VDDIO = df_concat['0:Istandby:VDDIO[1]']
# print('$$$VDDIO:', VDDIO)
df_concat.set_index('lot_id', inplace=True)
path_str = ''
if len(str(Wafer_ID)) == 1:
path_str = '_W0'
elif len(str(Wafer_ID)) == 2:
path_str = '_W'
output_path = path_pardir + '/Output/' + str(Lot_ID) + path_str + str(Wafer_ID) + '.xlsx'
df_concat.to_excel(output_path)
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 设置清洗后的表格的内部格式
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(output_path)
ws = wb.active
# 冻结窗口
ws.freeze_panes = 'F2'
# 字体微软雅黑, 加粗
font = openpyxl.styles.Font('微软雅黑', bold=True)
# 填充色为深橙色FF8C00
fill = openpyxl.styles.PatternFill(fill_type='solid', start_color='FF8C00')
# 计算每列最大宽度, 并存储在列表col_widths中
col_widths = []
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 定义初始列宽col_width, 并在每个行循环完成后重置
col_width = 1
# 从第二行开始, 因为第一行为列标签, 即不计算第一行的列标签的宽度, 后面让其自动换行即可
for j in range(2, ws.max_row + 1):
cell_value = ws.cell(row=j, column=i).value
# 中文占用多个字节, 需要分开处理
if isinstance(cell_value, str):
# gbk解码一个中文两字节, utf-8一个中文三字节, gbk合适
col_width_real = len(cell_value.encode('gbk'))
else:
col_width_real = len(str(cell_value))
if col_width < col_width_real:
col_width = col_width_real
col_widths.append(col_width)
# 设置列宽
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 将数字转化为列名, 26个字母以内也可以用[chr(i).upper() for i in range(97, 123)], 不用导入模块
col_name = get_column_letter(i)
# 设置列宽, 一般加两个字节宽度, 可以根据实际情况灵活调整
ws.column_dimensions[col_name].width = col_widths[i - 1] + 6
# 设置第一行的单元格格式
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 设置第一行的单元格为自动换行, 水平居中, 垂直居中
ws.cell(1, i).alignment = openpyxl.styles.Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', wrap_text=True)
# 设置第一行的单元格字体为微软雅黑, 加粗
ws.cell(1, i).font = font
# 设置第一行的单元格填充颜色为深橙色FF8C00
ws.cell(1, i).fill = fill
wb.save(output_path)
print('第{}/{}个xlsx文件处理完毕!'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 画Map
print('开始输出第{}/{}个xlsx文件的Map...'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
List_Isb_sel = []
List_FBC_sel = []
# 获取当前系统时间, 格式为年_月_日_时_分_秒, 把系统时间添加到文件夹的命名中, 以避免文件夹重复且方便归档记录
Nowtime = dt.datetime.now().strftime('%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S')
# 创建文件夹, 使每片wafer的数据都单独有一个文件夹存放
local_path = path_pardir + '/Output/' + str(Lot_ID) + path_str + str(Wafer_ID) + '_' + Nowtime
os.makedirs(local_path)
Die_X = df_concat['die_x'].tolist()
Die_Y = df_concat['die_y'].tolist()
Bin = df_concat['SBIN_NUM'].tolist()
# 获取df_concat的列标签
col_label = df_concat.columns.values.tolist()
# print(col_label)
# print(type(col_label))
for s in col_label:
if re.match(r'.*Istandby.*', s, re.I):
List_Isb_sel.append(s)
elif re.match(r'.*((Scan)|(M6N)|(Data_Retention)).*', s, re.I):
List_FBC_sel.append(s)
for i in range(len(Bin)):
Bin_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, Bin, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, local_path)
for i in range(len(List_Isb_sel)):
List_Isb_item = List_Isb_sel[i]
List_Isb_temp = df_concat[List_Isb_sel[i]].tolist()
ISB_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, List_Isb_temp, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, List_Isb_item, local_path)
for i in range(len(List_FBC_sel)):
List_FBC_item = List_FBC_sel[i]
List_FBC_temp = df_concat[List_FBC_sel[i]].tolist()
# print(List_FBC_temp)
FBC_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, List_FBC_temp, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, List_FBC_item, local_path)
print('第{}/{}个xlsx文件的Map输出完毕!'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
count += 1
print('程序运行完毕!')
print('=' * 30)
10.完整脚本如下
代码如下:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.patches as patches
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import datetime as dt
import openpyxl
from openpyxl.utils import get_column_letter
import re
import os
import glob
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
pd.options.display.max_columns = None
global df_concat
# 获取当前脚本文件所在目录
path_current = os.getcwd()
# 获取当前脚本文件所在目录的上一级目录
path_pardir = os.path.dirname(path_current)
print('$$$path_pardir:', path_pardir)
file_lists = glob.glob(path_pardir + '/Output/*.xlsx')
print('$$$file_lists:', file_lists)
# 先定义好需要提取的有效信息的列名
column_common = ['lot_id', 'wf_id', 'die_x', 'die_y', 'SBIN_NUM']
# column_private = ['Istandby:VDD[1]', 'Istandby:VDDI[1]', 'Istandby:VDD_SRAM[1]', 'Istandby:VDDIO[1]',
# 'Scan_HV', 'Scan_MV', 'Scan_LV', 'M6N_HV', 'M6N_MV', 'M6N_LV', 'Data_Retention_0', 'Data_Retention_1']
abnormal_character_set = ['/', '\\', ':', '*', '"', '<', '>', '|', '?']
def cycle_picture():
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8), dpi=100)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
theta = np.arange(0, 2 * np.pi, 0.01)
x = 5 + 5.5 * np.cos(theta)
y = 4 + 4.5 * np.sin(theta)
# plt.vlines(np.arange(-0.5, 11, 1), -0.5, 8.5, linestyles='--')
# plt.hlines(np.arange(-0.5, 9, 1), -0.5, 10.5)
plt.plot(x, y, color='Black')
ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('top')
plt.xticks(np.arange(-1, 12, 1))
plt.yticks(np.arange(-1, 9, 1))
ax.invert_yaxis()
# plt.show()
return ax
def FBC_draw(die_X, die_Y, list_FBC_temp, lot, wafer, list_FBC_item, local_Path):
color_dict = {'1': '#00FF00', '2': '#32CD32', '3': '#90EE90', '4': '#F0E68C', '5': '#FFFF00', '6': '#FFA500',
'7': '#FF8C00', '8': '#FF7F50', '9': '#FF4500', '10': '#FF6347', '11': '#CD5C5C', '12': 'FF0000',
'13': '#8B0000'}
ax = cycle_picture()
for X, Y, FBC_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, list_FBC_temp):
# 以下if结构中用FBC_v的大小来衡量每个die该赋的颜色, 文字, 以及文字大致居中时所需的X轴的坐标偏移量
if FBC_v >= 268435456:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '12'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 67108864 <= FBC_v < 268435456:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '12'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 8388608 <= FBC_v < 67108864:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '9'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 2097152 <= FBC_v < 8388608:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '9'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 1048576 <= FBC_v < 2097152:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '5'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 524288 <= FBC_v < 1048576:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '5'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 104858 <= FBC_v < 524288:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024 / 1024, 1)
color = '4'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'M'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 1000 <= FBC_v < 104858:
temp_pv = round(FBC_v / 1024, 1)
color = '4'
pv = str(temp_pv) + 'K'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 100 <= FBC_v < 1000:
pv = FBC_v
color = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 50 <= FBC_v < 100:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 10 <= FBC_v < 50:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.2
elif 0 < FBC_v < 10:
pv = FBC_v
color = '3'
shift_v = 0.1
elif FBC_v == 0:
pv = FBC_v
color = '1'
shift_v = 0.1
else:
pv = FBC_v
color = '12'
shift_v = 0.1
# 画出对应的die的形状Rectangle, 透明度alpha, 表面填充颜色, 边缘线条颜色, 线宽
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[color], edgecolor='k', linewidth=2))
# 画出每个die上的文字, 即需要显示的Fail bit count的大小
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, pv, fontsize=12)
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_FBC_item = str(list_FBC_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
# 画出每片Wafer的标题
plt.text(1, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_FBC_item) + '_FBC_Map', size=14)
# 调整subplot的参数
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
# 保存画好的FBC_Map图, bbox_inches='tight'以紧凑型保存, 并格式化命名
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_FBC_item) + '_FBC_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# ion函数开始matplotlib的交互模式, 即遇到plt.show()函数时会继续执行
# plt.ion()
# plt.show()
plt.close()
def ISB_draw(die_X, die_Y, list_Isb_temp, lot, wafer, list_Isb_item, local_Path):
color_dict = {'1': '#00FF00', '2': '#32CD32', '3': '#90EE90', '4': '#F0E68C', '5': '#FFFF00', '6': '#FFA500',
'7': '#FF8C00', '8': '#FF7F50', '9': '#FF4500', '10': '#FF6347', '11': '#CD5C5C', '12': 'FF0000',
'13': '#8B0000'}
ax = cycle_picture()
for X, Y, ISB_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, list_Isb_temp):
pv = abs(float(ISB_v))
if 200 <= pv < 999999:
# pv = str(round(pv / 1000, 2)) + 'K' if pv >= 1000 else round(pv, 1)
# pv = round(pv, 1)
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 150 <= pv < 200:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 100 <= pv < 150:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.4
elif 80 <= pv < 100:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 50 <= pv < 80:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.25
elif 30 <= pv < 50:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '4'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 10 <= pv < 30:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '3'
shift_v = 0.3
elif 0 <= pv < 10:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '1'
shift_v = 0.2
else:
pv = round(pv, 2)
para_v = '13'
shift_v = 0.2
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[para_v], edgecolor='k',
linewidth=2))
# 画出每个die上的文字, 即需要显示的Fail bit count的大小
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, pv, fontsize=10)
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_Isb_item = str(list_Isb_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
plt.text(1, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_Isb_item) + '_Map', size=14)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_' + str(list_Isb_item) + '_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# plt.ion()
# plt.pause()
# plt.show()
plt.close()
def Bin_draw(die_X, die_Y, bin, lot, wafer, local_Path):
ax = cycle_picture()
color_dict = {1: '#00FF00', 2: '#FF0000', 4: '#800000', 7: '#FFA500', 8: '#FF4500', 9: '#FFFF00',
10: '#7B68EE', 11: '#800080', 12: '#008080', 13: '#F08080', 14: '#BC8F8F', 15: '#CD5C5C',
16: '#87CEFA', 17: '#D4F2E7', 30: '#DA70D6', 31: '#9932CC', 32: '#0000FF', 36: '#FF00FF',
40: '#00FFFF', 44: '#1E90FF', 48: '#FF69B4', 49: '#FF6347', 66: '#FF69B4'}
for X, Y, bin_v in zip(die_X, die_Y, bin):
# 若First Fail Bin 不在color_dict的键值中, 则一律将其颜色赋值为color_dict中键值42的颜色值
if bin_v in color_dict.keys():
bin_v_index = bin_v
else:
bin_v_index = 66
ax.add_patch(patches.Rectangle([X - 0.5, Y - 0.5], 1, 1, alpha=0.8, facecolor=color_dict[bin_v_index], edgecolor='k', linewidth=2))
shift_v = 0.08 if len(str(bin_v)) == 1 else 0.2
plt.text(X - shift_v, Y + 0.08, bin_v, fontsize=18)
# 画图例
legend = [[1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 30, 31, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 49, 66]]
colcolor = ['#00FF00', '#FF0000', '#800000', '#FFA500', '#FF4500', '#FFFF00', '#7B68EE', '#800080', '#008080',
'#F08080', '#BC8F8F', '#CD5C5C', '#87CEFA', '#D4F2E7', '#DA70D6', '#9932CC', '#0000FF', '#FF00FF',
'#00FFFF', '#1E90EF', '#FF69B4', '#FF6347', '#FF69B4']
plt.table(loc='bottom', cellText=legend, cellLoc='center', colColours=colcolor, rowLabels=['Bin'])
# 画标题
plt.text(3.5, -0.77, str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_Bin_Map', size=14)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.95, bottom=0, left=0, right=1, hspace=0, wspace=0)
plt.savefig(local_Path + '/' + str(lot) + '_W' + str(wafer) + '_Bin_Map.jpg', bbox_inches='tight')
# plt.ion()
# plt.show()
# plt.pause()
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('程序正在运行, 请稍等...')
count = 1
for file in file_lists:
print('=' * 30)
print('正在处理第{}/{}个xlsx文件...'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 清洗.xlsx数据
df_dict = pd.read_excel(file, sheet_name=None)
sheet_name_list = list(df_dict)
# print('$$$sheet_name_list:', sheet_name_list)
sheet_name_sel_list = []
for sheet_name in sheet_name_list:
if re.match(r'.*STDF.*', sheet_name, re.I):
sheet_name_sel = re.match(r'.*STDF.*', sheet_name, re.I)
sheet_name_sel_list.append(sheet_name_sel.group())
# print('$$$sheet_name_sel_list:', sheet_name_sel_list)
######################################################################
# 先提取共通的信息['lot_id', 'wf_id', 'die_x', 'die_y', 'SBIN_NUM']
df_common_sel = df_dict[sheet_name_sel_list[0]]
df_common = df_common_sel[column_common]
# print('$$$df_common:', df_common)
######################################################################
# 再提取非共通的信息['Istandby:VDD[1]', 'Istandby:VDDI[1]', 'Istandby:VDD_SRAM[1]', 'Istandby:VDDIO[1]',
# 'Scan_HV', 'Scan_MV', 'Scan_LV', 'M6N_HV', 'M6N_MV', 'M6N_LV', 'Data_Retention_0', 'Data_Retention_1']
column_private_dict = {}
for sheet_name_var in sheet_name_sel_list:
df_private_sel = df_dict[sheet_name_var]
column_list = list(df_private_sel)
for cols in column_list:
if re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDD\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDDI\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDD_SRAM\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Istandby:VDDIO\[1]', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_HV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_MV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Scan_LV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_HV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_MV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*M6N_LV.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Data_Retention_0.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
elif re.match(r'.*Data_Retention_1.*', cols, re.I):
column_private_dict.setdefault(sheet_name_var, []).append(cols)
# print('$$$column_private_dict:', column_private_dict)
num = 1
for key in list(column_private_dict):
df_tmp = df_dict[key][column_private_dict[key]]
if num == 1:
df_concat = pd.concat([df_common, df_tmp], axis=1)
else:
df_concat = pd.concat([df_concat, df_tmp], axis=1)
num += 1
# print('$$$df_concat:', df_concat)
# print('$$$list(df_concat):', list(df_concat))
Lot_ID = df_concat['lot_id'][0]
Wafer_ID = df_concat['wf_id'][0]
# VDDIO = df_concat['0:Istandby:VDDIO[1]']
# print('$$$VDDIO:', VDDIO)
df_concat.set_index('lot_id', inplace=True)
path_str = ''
if len(str(Wafer_ID)) == 1:
path_str = '_W0'
elif len(str(Wafer_ID)) == 2:
path_str = '_W'
output_path = path_pardir + '/Output/' + str(Lot_ID) + path_str + str(Wafer_ID) + '.xlsx'
df_concat.to_excel(output_path)
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 设置清洗后的表格的内部格式
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(output_path)
ws = wb.active
# 冻结窗口
ws.freeze_panes = 'F2'
# 字体微软雅黑, 加粗
font = openpyxl.styles.Font('微软雅黑', bold=True)
# 填充色为深橙色FF8C00
fill = openpyxl.styles.PatternFill(fill_type='solid', start_color='FF8C00')
# 计算每列最大宽度, 并存储在列表col_widths中
col_widths = []
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 定义初始列宽col_width, 并在每个行循环完成后重置
col_width = 1
# 从第二行开始, 因为第一行为列标签, 即不计算第一行的列标签的宽度, 后面让其自动换行即可
for j in range(2, ws.max_row + 1):
cell_value = ws.cell(row=j, column=i).value
# 中文占用多个字节, 需要分开处理
if isinstance(cell_value, str):
# gbk解码一个中文两字节, utf-8一个中文三字节, gbk合适
col_width_real = len(cell_value.encode('gbk'))
else:
col_width_real = len(str(cell_value))
if col_width < col_width_real:
col_width = col_width_real
col_widths.append(col_width)
# 设置列宽
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 将数字转化为列名, 26个字母以内也可以用[chr(i).upper() for i in range(97, 123)], 不用导入模块
col_name = get_column_letter(i)
# 设置列宽, 一般加两个字节宽度, 可以根据实际情况灵活调整
ws.column_dimensions[col_name].width = col_widths[i - 1] + 6
# 设置第一行的单元格格式
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 设置第一行的单元格为自动换行, 水平居中, 垂直居中
ws.cell(1, i).alignment = openpyxl.styles.Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', wrap_text=True)
# 设置第一行的单元格字体为微软雅黑, 加粗
ws.cell(1, i).font = font
# 设置第一行的单元格填充颜色为深橙色FF8C00
ws.cell(1, i).fill = fill
wb.save(output_path)
print('第{}/{}个xlsx文件处理完毕!'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 画Map
print('开始输出第{}/{}个xlsx文件的Map...'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
List_Isb_sel = []
List_FBC_sel = []
# 获取当前系统时间, 格式为年_月_日_时_分_秒, 把系统时间添加到文件夹的命名中, 以避免文件夹重复且方便归档记录
Nowtime = dt.datetime.now().strftime('%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S')
# 创建文件夹, 使每片wafer的数据都单独有一个文件夹存放
local_path = path_pardir + '/Output/' + str(Lot_ID) + path_str + str(Wafer_ID) + '_' + Nowtime
os.makedirs(local_path)
Die_X = df_concat['die_x'].tolist()
Die_Y = df_concat['die_y'].tolist()
Bin = df_concat['SBIN_NUM'].tolist()
# 获取df_concat的列标签
col_label = df_concat.columns.values.tolist()
# print(col_label)
# print(type(col_label))
for s in col_label:
if re.match(r'.*Istandby.*', s, re.I):
List_Isb_sel.append(s)
elif re.match(r'.*((Scan)|(M6N)|(Data_Retention)).*', s, re.I):
List_FBC_sel.append(s)
for i in range(len(Bin)):
Bin_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, Bin, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, local_path)
for i in range(len(List_Isb_sel)):
List_Isb_item = List_Isb_sel[i]
List_Isb_temp = df_concat[List_Isb_sel[i]].tolist()
ISB_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, List_Isb_temp, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, List_Isb_item, local_path)
for i in range(len(List_FBC_sel)):
List_FBC_item = List_FBC_sel[i]
List_FBC_temp = df_concat[List_FBC_sel[i]].tolist()
# print(List_FBC_temp)
FBC_draw(Die_X, Die_Y, List_FBC_temp, Lot_ID, Wafer_ID, List_FBC_item, local_path)
print('第{}/{}个xlsx文件的Map输出完毕!'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
count += 1
print('程序运行完毕!')
print('=' * 30)
四、需要注意的点
1.由于文件夹名或者文件名中不能有以下九种字符,所以在保存图片之前需要对文件名中的这些字符进行过滤剔除
代码如下:
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_FBC_item = str(list_FBC_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
for abnormal_character in abnormal_character_set:
list_Isb_item = str(list_Isb_item).replace(abnormal_character, ' ')
2.由于我们直接利用pandas输出到excel文件中时,表格是没有任何格式设置的,如果我们希望看到格式比较规整的excel表格,就需要用下面这段代码进行格式设置(主要利用openpyxl进行格式化设置)
代码如下:
######################################################################
######################################################################
# 设置清洗后的表格的内部格式
wb = openpyxl.load_workbook(output_path)
ws = wb.active
# 冻结窗口
ws.freeze_panes = 'F2'
# 字体微软雅黑, 加粗
font = openpyxl.styles.Font('微软雅黑', bold=True)
# 填充色为深橙色FF8C00
fill = openpyxl.styles.PatternFill(fill_type='solid', start_color='FF8C00')
# 计算每列最大宽度, 并存储在列表col_widths中
col_widths = []
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 定义初始列宽col_width, 并在每个行循环完成后重置
col_width = 1
# 从第二行开始, 因为第一行为列标签, 即不计算第一行的列标签的宽度, 后面让其自动换行即可
for j in range(2, ws.max_row + 1):
cell_value = ws.cell(row=j, column=i).value
# 中文占用多个字节, 需要分开处理
if isinstance(cell_value, str):
# gbk解码一个中文两字节, utf-8一个中文三字节, gbk合适
col_width_real = len(cell_value.encode('gbk'))
else:
col_width_real = len(str(cell_value))
if col_width < col_width_real:
col_width = col_width_real
col_widths.append(col_width)
# 设置列宽
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 将数字转化为列名, 26个字母以内也可以用[chr(i).upper() for i in range(97, 123)], 不用导入模块
col_name = get_column_letter(i)
# 设置列宽, 一般加两个字节宽度, 可以根据实际情况灵活调整
ws.column_dimensions[col_name].width = col_widths[i - 1] + 6
# 设置第一行的单元格格式
for i in range(1, ws.max_column + 1):
# 设置第一行的单元格为自动换行, 水平居中, 垂直居中
ws.cell(1, i).alignment = openpyxl.styles.Alignment(horizontal='center', vertical='center', wrap_text=True)
# 设置第一行的单元格字体为微软雅黑, 加粗
ws.cell(1, i).font = font
# 设置第一行的单元格填充颜色为深橙色FF8C00
ws.cell(1, i).fill = fill
wb.save(output_path)
print('第{}/{}个xlsx文件处理完毕!'.format(count, len(file_lists)))
######################################################################
######################################################################
3.获取系统当前时间,把时间字符串添加到文件夹的命名中,这样可以避免多次运行程序导致文件夹重复,覆盖原有文件夹的问题
代码如下:
# 获取当前系统时间, 格式为年_月_日_时_分_秒, 把系统时间添加到文件夹的命名中, 以避免文件夹重复且方便归档记录
Nowtime = dt.datetime.now().strftime('%Y_%m_%d_%H_%M_%S')
# 创建文件夹, 使每片wafer的数据都单独有一个文件夹存放
local_path = path_pardir + '/Output/' + str(Lot_ID) + path_str + str(Wafer_ID) + '_' + Nowtime
os.makedirs(local_path)
五、总结
本文所要讲的内容就这些,主要讲了如何利用正则表达式re模块和pandas模块清洗数据混乱的表格.xlsx文件;然后讲了如何利用openpyxl对清洗后的表格进行单元格格式化设置,接着讲了如何利用matplotlib模块对清洗后的表格进行数据可视化分析。希望对大家学习数据清洗、数据分析有帮助。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献2条内容
已为社区贡献2条内容







所有评论(0)